What the Heck Does GPT Mean?
In today's newsletter we break down the meaning of GPT and the history behind it.
WORD OF THE DAY: GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer)
Definition: GPT stands for Generative Pre-trained Transformer. Think of it as a super-smart autocomplete on steroids. It’s an AI system that’s been trained on massive amounts of text from the internet and can predict what words should come next in a sentence, except it’s so good at this that it can write entire essays, answer questions, write code, and have conversations that feel human.
Here’s what each part means:
Generative: It creates (generates) new text, not just copies what it’s seen
Pre-trained: It learned from billions of examples before you ever used it
Transformer: The underlying architecture (think of it as the engine design) that makes it work
Why Business Owners Should Care:
GPT models power tools you’re probably already using: ChatGPT, Microsoft Copilot, customer service chatbots, content creation tools, and coding assistants. Understanding how these systems evolved helps you know what they can (and can’t) do, where they’re headed, and how to use them effectively in your business.
The key insight: GPT doesn’t “think” or “understand” like humans do. It’s incredibly good at predicting patterns in language based on what it’s seen before. That’s both its superpower and its limitation.
THE HISTORY OF GPT: From Lab Experiment to Business Tool
The Foundation: How We Got Here (1980s-2017)
Before GPT, AI researchers spent decades trying to teach computers to understand language. Early attempts were like teaching someone to speak by giving them a dictionary and grammar rules, technically correct but missing the nuance of how people actually communicate.
The breakthrough came in 2017 when researchers introduced Transformers—a new architecture that could understand context better. Think of it like this: if you read “I went to the bank,” the old systems couldn’t tell if you meant a river bank or a financial bank. Transformers could use surrounding words to figure it out, just like humans do.
Key innovations that made Transformers work:
Attention mechanisms: The ability to focus on relevant parts of text (like how you’d skim a document for key information)
Self-attention: Understanding relationships between words, even if they’re far apart in a sentence
Positional encoding: Knowing word order matters (”man eats apple” vs “apple eats man”)
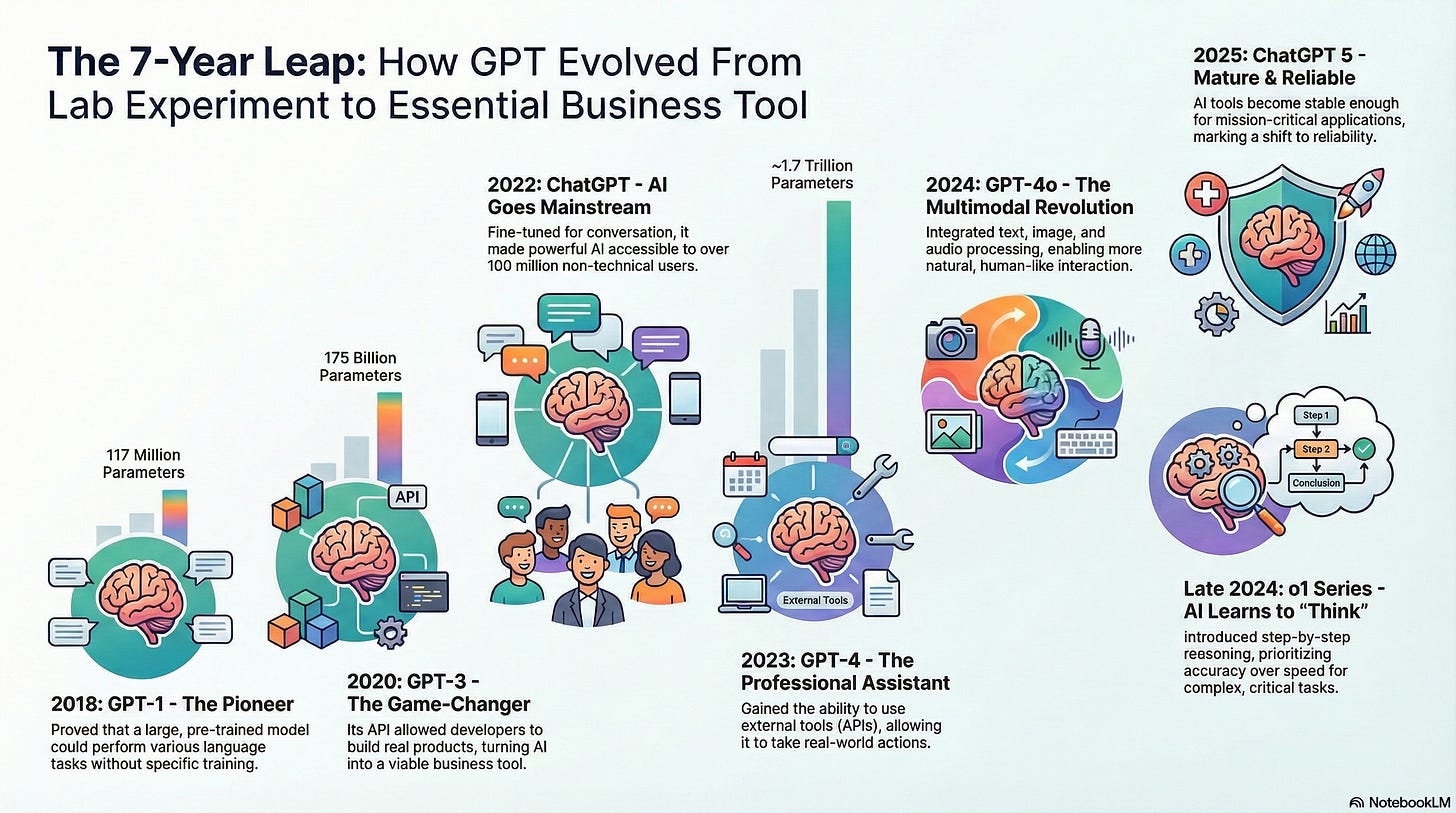
GPT-1 (2018): The Pioneer
OpenAI released GPT-1 in 2018 with 117 million parameters.
What’s a parameter? Think of parameters as the “knowledge” stored in the AI’s brain. More parameters = more capacity to understand complex patterns. 117 million sounds huge, but it’s tiny compared to what came later.
GPT-1 proved that if you train a language model on tons of text first (called pre-training), it becomes surprisingly good at many different tasks without being specifically taught those tasks. This was like discovering that someone who reads thousands of books naturally becomes good at writing, editing, summarizing, and analyzing—all without formal training in each skill.
Business Impact: Mostly academic. Cool concept, but not practical yet.
GPT-2 (2019): The Controversy
In 2019, OpenAI released GPT-2 with 1.5 billion parameters—more than 10x bigger than GPT-1.
GPT-2 was so good at generating human-like text that OpenAI initially refused to release it publicly, fearing it could be used to create fake news or impersonate people. This sparked huge debate: Was AI text generation now dangerous?
What GPT-2 Could Do:
Write coherent, contextually relevant paragraphs
Complete stories in different writing styles
Generate surprisingly believable (but often wrong) content
Business Impact: Still mostly experimental, but companies started paying attention. The potential for automated content creation became obvious.
GPT-3 (2020): The Game-Changer
GPT-3 launched in 2020 with 175 billion parameters—over 100x bigger than GPT-2. This wasn’t just incremental improvement; it was a quantum leap.
The Size Comparison:
GPT-1: 117 million parameters
GPT-2: 1.5 billion parameters
GPT-3: 175 billion parameters
With GPT-3, OpenAI introduced an API (Application Programming Interface), meaning developers could finally build real products using it. This was the moment AI went from lab curiosity to business tool.
GPT-3’s Superpowers:
Few-Shot Learning: You could teach GPT-3 new tasks with just a few examples, no retraining required. It’s like showing an employee 2-3 examples and having them understand the pattern instantly. Example: Show it three product reviews labeled “positive” or “negative,” then it can classify thousands more correctly.
Zero-Shot Learning: Even more impressive—GPT-3 could attempt tasks it had never seen before, just from a description. Example: “Translate this to French” worked, even though you didn’t give it any translation examples.
Long Context: GPT-3 could handle 2,048 tokens (roughly 1,500 words) at once, understanding longer documents.
The Limitation: GPT-3 was a “completion model”—it just tried to finish whatever text you started. It couldn’t really hold a conversation or follow complex instructions. You had to trick it into being useful by carefully wording your prompts.
Business Impact: HUGE. Companies started building real products: automated customer service, content creation tools, coding assistants, data analysis tools. The AI gold rush began.
ChatGPT (2022): AI Goes Mainstream
In late 2022, OpenAI released ChatGPT—a version of GPT-3 that was fine-tuned specifically for conversation.
What’s Fine-Tuning? It’s like taking someone who’s read everything on the internet and then giving them specific training on how to be a helpful assistant. The base knowledge is there; fine-tuning teaches them HOW to use it.
The Shift: Completion Model → Instruction Model
Old way (GPT-3): You had to game the system
Prompt: “The following is a conversation between a helpful AI and a user. User: What’s 2+2? AI:”
Response: “4”
New way (ChatGPT): Just ask naturally
Prompt: “What’s 2+2?”
Response: “2+2 equals 4.”
ChatGPT understood you wanted help, not text completion. This seems simple, but it changed everything.
Business Impact: AI became usable by non-technical people. Your marketing team, accountant, and receptionist could now use AI without learning complex prompting techniques. Over 100 million users signed up in 2 months—the fastest-growing consumer app in history.
GPT-4 (2023): Pushing the Boundaries
Released in 2023, GPT-4 was estimated at 1.74 trillion parameters—another 10x jump.
Major Improvements:
Longer Context: From 4,000 tokens to 32,000 tokens (about 25,000 words). You could now feed it entire business reports.
Function Calling: GPT-4 could use external tools and APIs. Instead of just answering “What’s Apple’s stock price?”—it could actually fetch the current price from a stock API. This meant AI could now:
Pull real-time data
Control other software
Take actions, not just generate text
Become a true “assistant” that does things
Better Reasoning: More accurate, more nuanced, fewer confident mistakes.
Business Impact: AI agents became possible. Companies built systems where AI could actually complete multi-step tasks: research competitors, draft reports, schedule meetings, analyze data—not just chat.
GPT-4o (2024): The Multimodal Revolution
In 2024, OpenAI released GPT-4o (the “o” stands for “omni”—meaning “all”).
The Big Deal: It’s Multimodal
Previous GPTs only handled text. GPT-4o can:
Process and generate TEXT
Analyze IMAGES
Understand and generate AUDIO
Combine all three naturally
Real-World Example: You could show GPT-4o a photo of a hand-drawn wireframe for a website, describe what you want in your voice, and it would write the code to build it—understanding both the visual layout and your verbal instructions.
Real-Time Interaction: GPT-4o can have voice conversations with minimal delay, making it feel like talking to a person rather than waiting for a computer to process your request.
Business Impact: AI can now handle visual content (analyzing charts, reading documents, understanding diagrams), voice interfaces (customer service calls), and multimedia content creation—all in one system.
o1 Series (Late 2024): The Reasoning Models
In late 2024, OpenAI introduced a completely new approach with the o1 series (originally called “Strawberry”). Unlike previous models that respond immediately, o1 models actually “think” before answering.
How It Works: When you ask o1 a question, it spends time reasoning through the problem—sometimes 30+ seconds—showing you its “chain of thought” process. It’s like watching someone work through a math problem step-by-step rather than just giving you the answer.
What o1 Excels At:
Complex problem-solving (coding, math, science)
Multi-step reasoning that requires planning
Catching its own mistakes before responding
Tasks where accuracy matters more than speed
The Trade-off: o1 is slower and more expensive to run, but significantly more accurate on difficult tasks. It’s the difference between asking for a quick opinion versus asking someone to carefully think through a problem.
Business Impact: For critical decisions, technical work, or complex analysis, o1 provides a new level of reliability. It’s not for casual chat—it’s for when you need AI to really think things through.
ChatGPT 5 and Beyond (2025): Refinement and Integration
As of December 2025, we’re at ChatGPT 5.2, representing continued refinement rather than revolutionary changes.
What’s Changed Since GPT-4o:
Improved accuracy across all tasks, with fewer hallucinations
Better context retention in longer conversations
Enhanced reasoning combining speed (GPT-4o style) with deeper thinking (o1 style)
More reliable tool use when working with external APIs and data
Refined personality that’s more helpful, nuanced, and adaptive to user needs
The Pattern We’re Seeing: Rather than massive leaps in capabilities, 2025 has been about making AI more reliable, easier to use, and better integrated into everyday workflows. The focus shifted from “What can AI do?” to “How can AI do it better and more consistently?”
Business Impact: AI tools are now mature enough for mission-critical applications. The Wild West phase is ending; we’re entering the “boring but reliable” phase—which is exactly what businesses need.
WHERE WE ARE TODAY (END OF 2025): Four Key Trends
1. From Narrow to General AI
2018: AI could do one task well if trained specifically for it
2024: AI can handle hundreds of tasks with no specific training
2025: Moving toward AI that can reason, plan, and self-correct—getting closer to true general intelligence
2. Multimodal Everything
Text-only → Text + Images + Audio + Video
This mirrors how humans actually communicate and work
By 2025, multimodal is the default, not a special feature
3. Increased Accessibility
2020: Only developers could use GPT-3
2024: Anyone with internet access can use ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini
2025: APIs are cheaper, easier to use, and more powerful—AI is becoming infrastructure
4. Reasoning Over Speed
Early models: Fast but often wrong
2024: Introduction of reasoning models (o1) that think before responding
2025: Balance between fast responses and deep reasoning depending on task
THE PLATEAU QUESTION: Did We Slow Down or Speed Up?
Here’s the fascinating tension in AI development as we end 2025:
The Case for a Plateau: Research from 2024 suggested that simply making models bigger and feeding them more data wasn’t delivering the same rate of improvement. The gains were following a logarithmic curve—meaning you need exponentially more data and compute power for smaller improvements.
Evidence: GPT-4o showed minimal improvement over GPT-4 Turbo in English text and coding. Despite being larger and trained on more data, the core improvements were plateauing in traditional benchmarks.
The Plot Twist: Then came the o1 reasoning models and continued refinements in 2025.
What Actually Happened:
Instead of hitting a wall, AI companies found a new direction: reasoning and reliability over raw size. The breakthrough wasn’t making models bigger—it was making them think differently.
The o1 Approach: Rather than just predicting the next word, o1 models use “chain of thought” reasoning—actually working through problems step by step. This delivered major improvements without requiring massively larger models.
The Result: By late 2025, we have models that are:
More accurate on complex tasks
Better at catching their own mistakes
More reliable for business-critical applications
Capable of genuine multi-step reasoning
Microsoft’s Bet Pays Off: Microsoft’s investment in massive computing infrastructure for training GPT-5 and beyond suggests they found ways to keep improving performance—just not always in the ways we expected.
The Real Story: The plateau fears were partially right—we couldn’t just keep scaling the same approach forever. But AI didn’t slow down; it pivoted to new methods that continue delivering meaningful improvements.
WHAT THIS MEANS FOR YOUR BUSINESS (END OF 2025)
The Good News: Maturity + Innovation
By the end of 2025, we’re in a sweet spot: AI tools are mature enough to rely on, but still improving meaningfully.
1. Production-Ready: Current AI isn’t experimental anymore. ChatGPT 5.2, Claude, and Gemini are reliable enough for customer-facing applications, critical business processes, and daily operations.
2. Continuous Improvement: Unlike the plateau fears of 2024, AI continues getting better—just through refinement and new reasoning approaches rather than revolutionary leaps.
3. Human Expertise Enhanced: AI has become a true force multiplier. The businesses winning with AI aren’t replacing humans; they’re making their human expertise dramatically more effective.
4. Accessible to Everyone: The technical barriers are gone. Your entire team can use AI effectively without coding knowledge or advanced technical skills.
The Strategy: Implement, Integrate, Iterate
The playbook for AI in business has crystallized in 2025:
Choose Your Tools: ChatGPT, Claude, or Gemini—pick one and learn it deeply. They’re all excellent; the differences matter less than your expertise with the tool you choose.
Start with Quick Wins: Automate the repetitive tasks that drain your team’s time—email drafting, meeting summaries, first-draft content, data analysis, customer service responses.
Build Reliable Workflows: Document your AI processes. When something works, systematize it so your entire team can use it consistently.
Use Reasoning for Critical Tasks: For important decisions, complex analysis, or technical work, use reasoning models (like o1) that think through problems carefully.
Train Your Team Continuously: AI tools update monthly. Dedicate time for your team to learn new features and share best practices.
Measure Real Impact: Track time saved, quality improvements, and cost reductions. AI’s value should be measurable, not theoretical.
What’s Coming in 2026 and Beyond
Based on where we are at the end of 2025, here’s what’s likely next:
Near-Term (2026):
Agentic AI goes mainstream: AI that can complete multi-day projects autonomously, checking in only when it needs human decisions
Deeper business integration: AI becomes native in every major software platform—your CRM, accounting software, project management tools
Industry-specific models: AI trained specifically for healthcare, legal, finance, manufacturing, etc.
Voice-first interfaces: Talking to AI becomes as common as typing
Medium-Term (2027-2028):
Personal AI assistants: AI that knows your business inside and out, trained on all your company data
True collaboration: AI that works alongside humans as a team member, not just a tool
Multimodal creation: Generate complete marketing campaigns (video, audio, text, images) from a single prompt
Real-time learning: AI that learns from your feedback immediately, not through retraining
The Big Unknown: AGI Artificial General Intelligence—AI that truly matches human intelligence across all domains—remains the ultimate goal. As of 2025, we’re meaningfully closer than in 2024, but still not there.
The question isn’t “if” anymore—most experts agree we’ll reach AGI. The question is “when”: 2030? 2035? 2040? Nobody knows for sure, but the pace of progress suggests it’s measured in years, not decades.
THE BOTTOM LINE
We’ve gone from AI that could barely complete sentences (2018) to AI that can hold conversations, analyze images, reason through complex problems, and complete sophisticated tasks (2025), all in just seven years.
The plateau fears of 2024 turned out to be a false alarm. AI didn’t slow down; it just changed direction—focusing on reasoning, reliability, and real-world application rather than simply getting bigger.
As we close 2025, the tools are mature, the use cases are proven, and the competitive advantage is real. Companies using AI effectively are pulling ahead of those still waiting to “see how it plays out.”
The question isn’t “Will AI get better?” (it will) or “Should I wait for the next big breakthrough?” (you shouldn’t).
The question is: What will you accomplish with AI in 2026 that would have been impossible in 2025?
The opportunity is real. The tools are ready. The only question is: what will you build with them?
Coming Next: Open source versus closed source and why it matters.
Thanks for reading. Have a tool or news story we should cover or need help implementing AI at your business? Reply to this email.


This explanation realy made the 'why business owners should care' part click in a new way for me. It's fascinating how you broke down the architechture, and that 'super-smart autocomplete on steroids' analogy is spot on, even though I teach kids who sometimes feel like they're just predicting patterns too.
Thank you for reading, commenting and, MOST IMPORTANTLY, for being a teacher! I'm so interested in how AI is affecting the teaching / education industry. Would love a guest post if you're ever up for it!